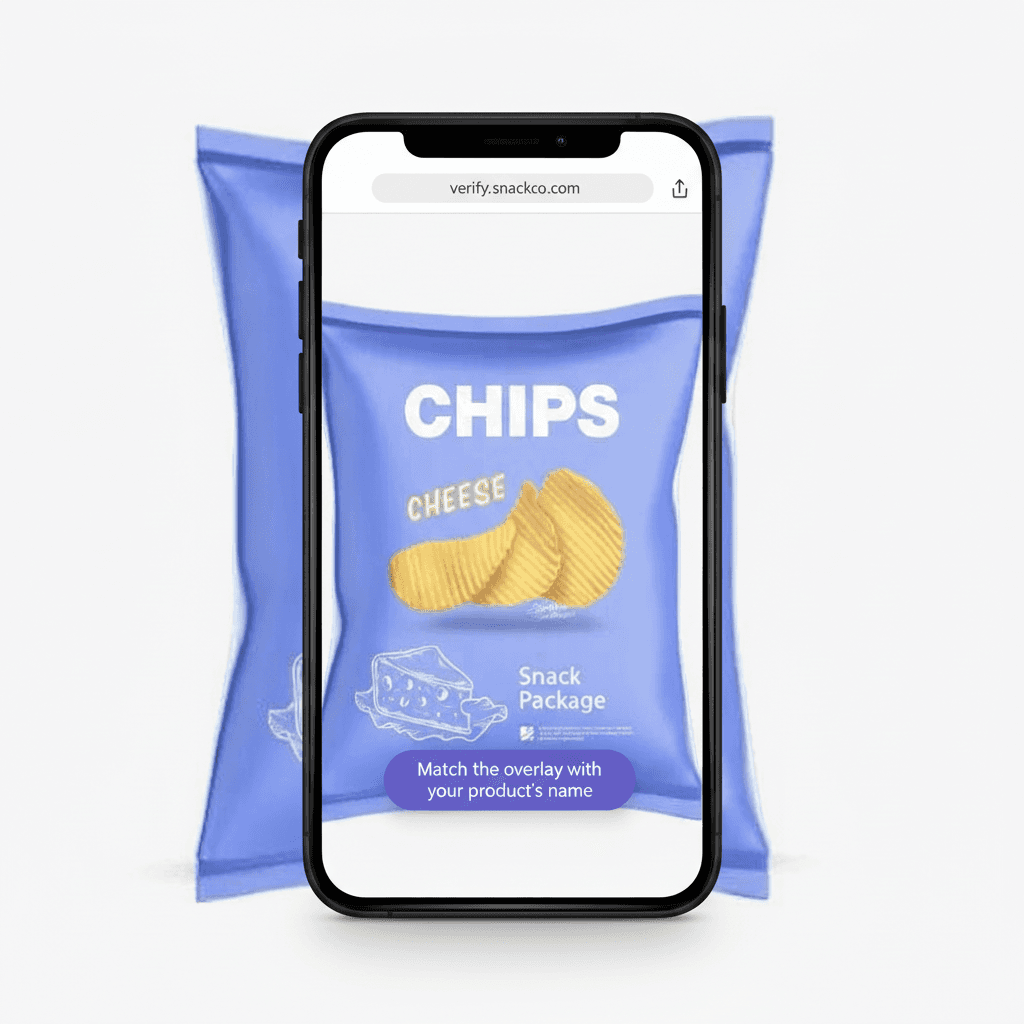
Scan using a normal smartphone camera.

Built on cutting-edge technology
Do we need new printing hardware or special inks?
No. Ennoventure's technology works with standard printing equipment, conventional inks (CMYK, Pantone, specialty formulations), and existing substrates. Authentication signals embed within regular artwork using normal production processes-offset, flexographic, gravure, screen printing, or digital. No manufacturing process changes, specialized materials, or equipment modifications are required, enabling rapid deployment and cost-effective scaling.

How does invisible authentication differ?
It embeds undetectable security into artwork and verifies with any smartphone. No app, no friction so attackers have nothing to study.

How fast is product verification?
Average scan-to-verdict time is 2.3 seconds under normal field conditions using standard smartphones. This includes camera image capture, cloud upload, signal extraction, error correction, ensemble AI analysis, and results delivery. Verification speed enables real-time authentication for consumer purchases, supply chain inspection, customs clearance, and retail point-of-sale scenarios without workflow disruption.

How does authentication integrate with existing brand protection programs?
Ennoventure's technology complements traditional brand protection by providing: (1) Covert authentication that counterfeiters cannot study or replicate, (2) Real-time verification accessible to all stakeholders without specialized training, (3) Market intelligence through authentication analytics revealing counterfeiting patterns and geographic hotspots, (4) Evidence generation for legal enforcement and customs seizures, and (5) Consumer engagement through brand-owned authentication experiences. Integration occurs through APIs, SDKs, or dashboard access depending on brand requirements.

How does this compare to QR codes, RFID, or blockchain-based authentication?
QR codes and visible tags are easily copied, removed, or counterfeited. Criminals simply reproduce the codes on fake products. RFID requires expensive tag procurement and reader infrastructure while remaining vulnerable to cloning. Blockchain provides transaction immutability but doesn't authenticate physical products themselves, counterfeiters can create fake products with blockchain-verified serial numbers. Invisible authentication operates at the artwork layer with cryptographic signals counterfeiters cannot detect or reproduce, requires only smartphones for verification, and embeds authentication inseparably within product packaging at minimal incremental cost.